25 August, 2021
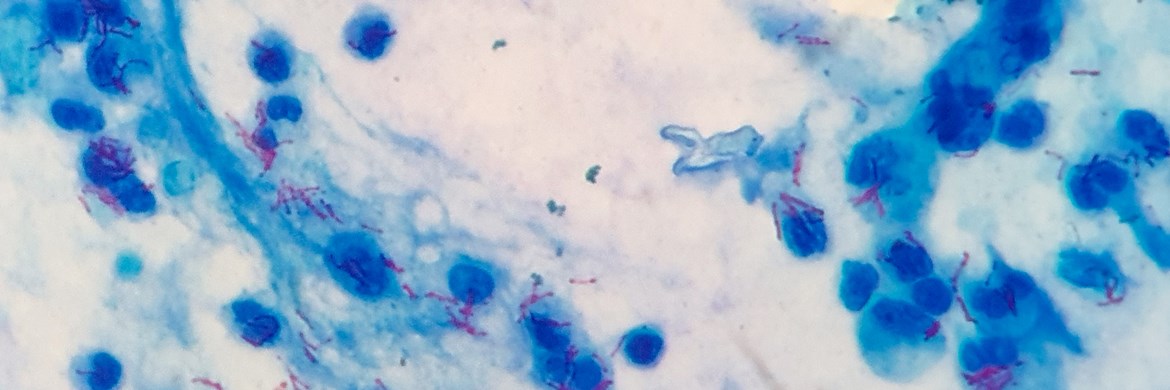
Recently, The WHO and Imperial College London have been working together to develop the largest catalogue for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) genome list with more than 17,000 mutations. This catalogue will help health services and professionals around the world to interpret genome sequencing results and treat patients quickly using the appropriate medications. This is a necessity in today’s society due to the increase of drug resistance to tuberculosis medications within the population.
Dr Leonid Chindelevitvh, from the School of Public Health who worked on the new TB catalogue says, ‘Tuberculosis is the largest infectious killer in the world today and drug resistance is becoming a significant global problem. The WHO catalogue will help medics and health services around the world to interpret results and provide faster and more targeted treatment for patients of this deadly disease.’
Tuberculosis (TB) is defined as a bacterial infection spread through inhaling tiny droplets from the coughs or sneezes of an infected person, caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. Individuals with weakened immune systems including, people living with HIV, people who use tobacco or people living with malnutrition, are more likely to become unwell with tuberculosis. The most common symptoms of the bacterial infection include;
- A persistent cough (that lasts more than three weeks)
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
- Tiredness and fatigue
Despite tuberculosis being a completely treatable and curable illness, many individuals die from the disease due to lack of support or medical input. Some people aren’t even aware they are living with TB. Treatment for tuberculosis consists of a standard 6-month course, if there is no drug resistance within the TB strain. If there is drug resistance, more serious treatments for TB are commenced, such as chemotherapy. The catalogue created by WHO and Imperial College London aims to reduce the use of antibiotics for treatments if the tuberculosis strain found within the patient is drug resistant. This improves the time for the patient from receiving diagnosis to starting a treatment that will be successful in stopping the bacterial infection and lowering the chance of severe illness or death.
This catalogue is to help minimize the effects of drug resistance in tuberculosis sufferers is essential in today’s society because, ‘Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) remains a public health crisis and a health security threat. A global total of 206 030 people with multidrug- or rifampicin-resistant TB (MDR/RR-TB) were detected and notified in 2019, a 10% increase from 186 883 in 2018'. This worrying statistic reiterates the importance of accurate and reliable testing solutions.
To detect infection at the early stages so treatments can be implemented in a timely manner, it is important to use testing solutions you can trust. Fortress Diagnostics offer the;
- Rapid Testing Tuberculosis Device (different sizes available)
For tuberculosis testing.
Imperial College London have also worked on other scientific studies such as the REACT2 programme, focusing on COVID-19. For this programme, Imperial College London have used Fortress Diagnostics COVID-19 testing products. You can also browse and request more information regarding these products through marketing@fortressdiagnostics.com.